
 Technical Information
Technical Information Power And Control Cables
Power And Control Cables Power Appendixes
Power Appendixes Guide to the Wiring Regulations
Guide to the Wiring Regulations General requirements of earthing and bonding
General requirements of earthing and bonding صفحه General requirements of earthing and bonding
| General requirements of earthing and bonding | |
|
The protective measures for general application are: * Automatic disconnection of supply; * Double or reinforced installation; * Electrical separation; * Extra-low voltage provided by SELV or PELV |
 |
| The protective measure ‘automatic disconnection of supply’ is by far the most common and makes specifc requirements for both protective earthing and protective bonding. | |
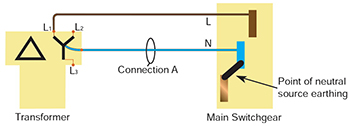
| A typical arrangement for an on-site transformer with the neutral earth link made in the main switchgear | |
| Again, we need to briefy review the requirements of the protective measure in order to establish earthing and bonding requirements. The basis of the measure is as follows. | |
|
* Basic protection (protection against direct contact) is protection from contact with live parts provided by basic insulation, or by barriers or enclosures. * Fault protection (protection against indirect contact) is provided by protective earthing, protective equipotential bonding and automatic disconnection in case of fault. In the event of a fault between a live conductor and an exposed-conductive- part of equipment, suffcient fault current fows to operate (trip or fuse) the overcurrent protection. For the protective measure to work, protective conductors are required to connect all exposed-conductive-parts (of equipment) to the earthing terminal. This is protective earthing and includes circuit protective conductors and the earthing conductor. To reduce shock voltages (touch voltages during a fault), and to provide protection in the event of an open circuit in the PEN conductor of a PME supply, protective equipotential bonding is also required. A simple installation with both circuit protective conductors and protective bonding conductors is shown in Following Figure : |
|
 |
|





